Updated: 2023-12-07
Many people have absolutely no idea about what a UX designer really does. Some have an idea, but they often confuse the function of UX with UI.
That’s why the first and most important point to be cleared is the difference between UX and UI designers by introducing them both in a simple example.
What’s the difference between UX designer and UI developer?
Imagine our product is a gourmet burger. Our company, staying current with market trends, caters to diverse customer preferences. UI designers are like skilled chefs, adept in culinary techniques and tools, ensuring the burger is visually appealing and crafted with precision. They focus on the aesthetics: the perfect grill marks on the patty, the melt of the cheese, and the presentation of the burger.
UX designers, on the other hand, are akin to culinary architects. They decide on the unique blend of ingredients based on customer preferences, dietary trends, and nutritional value. Their role involves understanding the customer’s desires, like the demand for plant-based options or gluten-free buns, and ensuring the burger’s flavors harmonize while being easy to eat and satisfying.
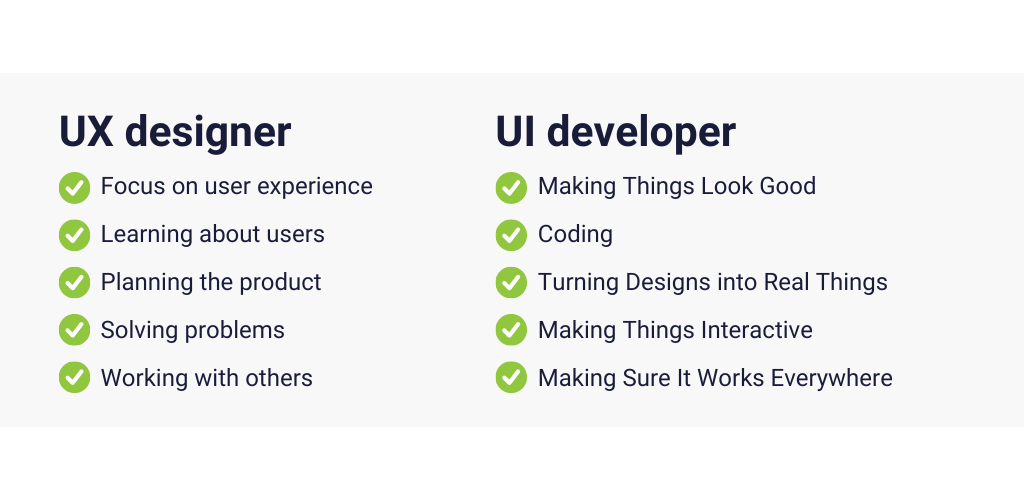
UX designer
- Focus on user experience: They focus on how people feel when they use a product. They think a lot about what users need and want.
- Learning about users: UX designers ask users questions and watch how they use things to understand them better.
- Planning the product: They make basic plans for what a product should do and how it should work, before it looks pretty.
- Solving problems: They find and fix problems to make sure using the product makes sense and is easy.
- Working with others: They work with different people, like UI designers and people who build the product, to make sure everything works well together.
UI developer
- Making Things Look Good: They focus on how the product looks and feels to use, like colors and buttons.
- Coding: UI Developers know how to write code to build websites or apps.
- Turning Designs into Real Things: They take designs from UX and UI designers and use code to make them real and work on computers and phones.
- Making Things Interactive: They create parts of a website or app that people can click on or interact with.
- Making Sure It Works Everywhere: They make sure the website or app works well on all kinds of devices, like phones and computers, and doesn’t have any problems.
Summary
Both roles are crucial. A visually stunning burger that misses the mark on taste or user dietary needs fails to impress, just as a delicious but unappealing burger might be overlooked. The collaboration between UI and UX ensures a product that is not only delightful to look at but also meets the evolving tastes and needs of customers.
What does a UX Designer really do?
UX designers (UXDs) do a lot of different things. They need to know about marketing, design, and managing projects. Donald Norman, who came up with the term ‘UX Design’, wanted it to mean more than just how something looks or works. He wanted it to include everything about how a person experiences a product. User Experience Designers start working on a project before it even begins and keep working after making models or prototypes. Their job isn’t just one part of the project; it’s about looking at the whole experience.
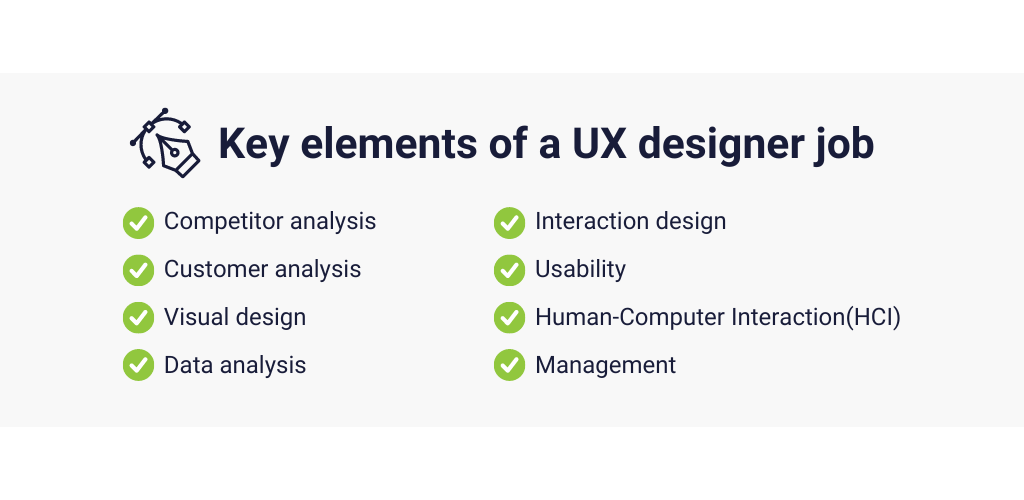
Key elements of a UX designer job
1. Competitor analysis
A UX designer (UXD) needs to be good at many things. Early in a project, they analyze competitors. This helps them see what they’re doing well and what needs improvement. It also helps them understand the market better. This kind of analysis is important to avoid mistakes and to know what makes their work special.
2. Customer analysis
A key task for a UX designer (UXD) is making personas for the project. These are made-up types of customers who will use the product. They make these personas by creating profiles with important info about the users. This info helps shape the design of the product. Often, they get this info by talking to people in interviews.
Then the rest of the work is done according to the potential clients’ taste.
3. Visual design
Visual design in UX is about how a product looks and feels during use. The UX designer decides on colors, where to put images, and how to mix visual elements for the best result. This part of their job is often seen as the most eye-catching by people outside the field.
4. Data analysis
This part is like architecture because it’s about organizing the product’s structure and information. The goal is to make it easy to use by simplifying and arranging components in a clear layout. A UX designer does well if users can find things easily and navigate a website or app without trouble.
5. Interaction design
This area is made up of 5 equally important steps-or so-called dimensions-, each one following and connecting to one another.
- Words: the most fundamental part of communication. The other four steps are also based on the words that we use, so it is substantial to pay attention to them.
- Visual representation: This may include the typography, icons or additional graphics. It is essential that the words and their visual representation are in harmony. It is a minor concern, but it can ruin everything in a second.
- Physical object and space: Physical object and space are also vital parts of the interaction design. Basically this decides how the interface will look like, how crowded a page should be, how and where to insert plain white background, how much space to leave etc.
- Time: In some circumstances, time is not that crucial, but in the case of videos, animations or even sounds, it is highly recommended to keep an eye on time. If you have dynamic content on your page or in your application, it is advisable to take care of it cautiously.
- Behavior: To maximize usability and the value of your product, you have to know how exactly your users/customers behave, what they actually do, etc. Of course, you can have A/B testing and prototype testing with real users, but we both know that in those cases something’s still missing. Do you really know what is missing, what is confusing the people, why do they leave your website?
6. Usability
Usability in UX design is crucial for meeting users’ needs, often achieved by making navigation simple and effective, leading to a satisfying user experience. The ISO definition emphasizes usability as the degree to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve goals with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a specific context.
There are five key aspects to consider:
- Learnability: ease of learning to use the product
- Efficiency: speed of performing tasks
- Memorability: ease of remembering how to use it
- Satisfaction: enjoyment and comfort using the product
- Error minimization
Achieving these aspects ensures user satisfaction.
7. Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
The last major part focuses on the interaction between electronic devices and humans, aiming to make this interaction as natural as possible through engineering and psychology. This area also considers social and cultural values. It uses mental models from Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) to apply real-life knowledge of users onto the screen, creating metaphors that reflect users’ mental models, aiding UX designers in their work.
+1: Management
Management skills are crucial for a UX designer. They need to present and communicate effectively to sell their ideas and highlight potential issues. Negotiation skills are necessary for interacting with stakeholders and reaching compromises. Coordinating with team members, like UI designers, is also essential. Without these skills, a UX designer’s efforts may not be fully realized.
Putting all these into practice
The 3 most important methods for this are:
- Wireframing: creating a basic layout blueprint for a screen, like a website’s initial framework
- Prototyping: an early version of a wireframe
- Testing: testers gather data and feedback on the product and its features
There are many tools to help UX designers streamline the prototyping phase. After creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes, testing can begin.
Conclusion
Some large companies may not recognize UX design as a professional job, seeing it as common sense tasks. However, the role of a UX designer is complex and involves facing changing circumstances and diverse challenges. A UX designer has a broad range of responsibilities that are crucial for the success of a product. If you’re launching a product and want the best outcomes, hiring a UX designer is a worthwhile consideration.
Don't forget, sharing is caring! :)


3 Comments
Ngeshlew
2016-09-09 at 11:43Very interesting.
I will do deeper research on this. Thanks Melinda